How Expert Pest Control Safeguards Your Home and Wellbeing
Pests aren’t just a nuisance—they can damage your property and threaten your family’s health. From costly structural repairs to the risk of disease, infestations require professional care. Knowing how skilled pest management protects both your home and health is key to keeping your space safe.
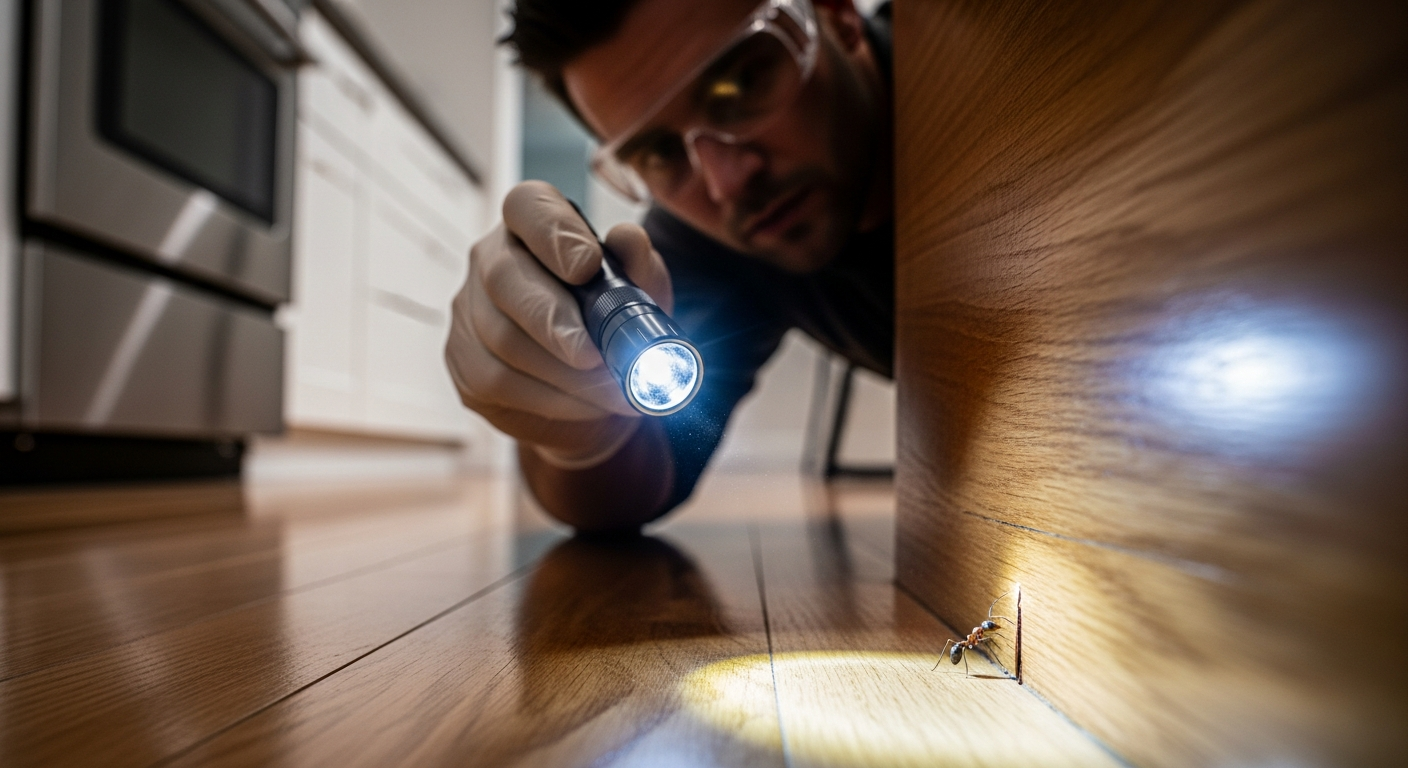

Protecting a home from pests is as much about prevention as it is about treatment. Professionals approach the task like a diagnostic process: they identify the species, uncover the conditions that help them thrive, and prescribe precise measures to remove the problem and keep it from returning. This integrated mindset reduces disruption, minimizes chemical use, and emphasizes long-term resilience for households in your area.
How professional pest control inspections are performed
A professional inspection typically begins with a detailed conversation about what you’ve noticed, when activity occurs, and any past treatments. Technicians then conduct a room-by-room assessment indoors, checking kitchens, bathrooms, basements, attics, and utility spaces for entry points, droppings, gnaw marks, frass, staining, or cast skins. Outside, they look at siding, soffits, gutters, vents, foundations, mulch, and vegetation. Tools such as moisture meters, flashlights, mirrors, and monitoring traps can reveal hidden activity in voids or under appliances.
Accurate identification drives the plan. Ants require different strategies than cockroaches; rodents demand exclusion and trapping; termites and wood-destroying organisms call for specialized detection. Inspectors document conducive conditions—standing water, gaps around pipes, torn screens, door sweep gaps, clutter, or food storage issues—and provide a written report with findings, site photos, and a recommended treatment and monitoring schedule. This baseline becomes the reference for follow-up visits and adjustments.
Common methods specialists use for household pests
Modern programs prioritize Integrated Pest Management (IPM), combining sanitation, exclusion, mechanical controls, and targeted chemistries when necessary. For crawling insects, crack-and-crevice applications concentrate products where pests harbor, while baits placed in discreet stations leverage insect behavior to spread control back to nests. Insect growth regulators can interrupt life cycles, and desiccant dusts help in voids where moisture is low. Heat or steam may be used for bed bugs in conjunction with vacuuming and encasements.
Rodent management relies on sealing entry points, improving sanitation, and deploying mechanical traps or tamper-resistant bait stations in locations that restrict access by children and pets. For termites, approaches include soil-applied termiticide barriers and baiting systems that monitor activity and deliver active ingredients only when colonies feed. Specialists select methods based on species, infestation size, building materials, and household risk factors. These are the common methods specialists use to address household pest issues, with emphasis on precision rather than broad, repeated spraying.
Safety practices used in modern pest management
Safety begins with product selection and placement. Professionals use EPA-registered products and follow label directions for application rates, target sites, and reentry intervals. Low-odor, targeted formulations and baits reduce airborne exposure, while crack-and-crevice techniques keep residues out of general living areas. Technicians wear appropriate PPE, ventilate treated spaces as needed, and provide service records detailing active ingredients and safety data.
To further reduce risk, providers favor non-chemical tactics first—sanitation, sealing, vacuuming, trapping, and habitat modification—reserving pesticides for well-defined needs. They protect water sources by avoiding drain application unless labeled, prevent drift, and secure bait in tamper-resistant stations. Clear communication is part of safety: households receive prep instructions (e.g., clearing cabinets or laundering linens), pet and child precautions, and post-service guidance on when normal activities can resume. These safety practices used in modern pest management help align effective control with household health.
Factors influencing long-term home pest prevention
Long-term success depends on the home, climate, and habits within it. Moisture management is central: fix leaks, insulate sweating pipes, vent bathrooms and dryers outdoors, and maintain gutters. Exclusion is equally important—seal gaps at utility penetrations, add door sweeps, repair screens, and reinforce weak spots around foundations, sill plates, and weep holes. Outdoors, keep mulch and firewood away from the structure, trim vegetation, and manage standing water to limit mosquito breeding.
Sanitation choices matter. Store food in sealed containers, clean crumbs and grease from kitchens and appliances, and take trash out regularly with tight-fitting lids. Reduce clutter that provides harborage for roaches and spiders, and rotate stored items off floors to reveal activity. Service frequency also plays a role; monitoring traps and scheduled inspections catch issues early. These are the factors that influence long-term prevention in home pest control, and they work best when occupants and professionals coordinate efforts and share observations between visits.
In sum, expert pest management safeguards both property and wellbeing by combining careful inspection, targeted interventions, and practical prevention. When inspections inform treatment—and treatment is backed by maintenance, monitoring, and communication—homes remain more comfortable, healthier, and better able to resist future infestations with minimal disruption.