Prefab homes: design trends, construction methods, and sustainable features
Prefabricated homes combine modern design approaches, efficient construction methods, and sustainable materials. This overview explains how prefab housing is built, which factors influence overall cost, and what features can improve comfort, energy use, and long-term practicality for different homeowners.
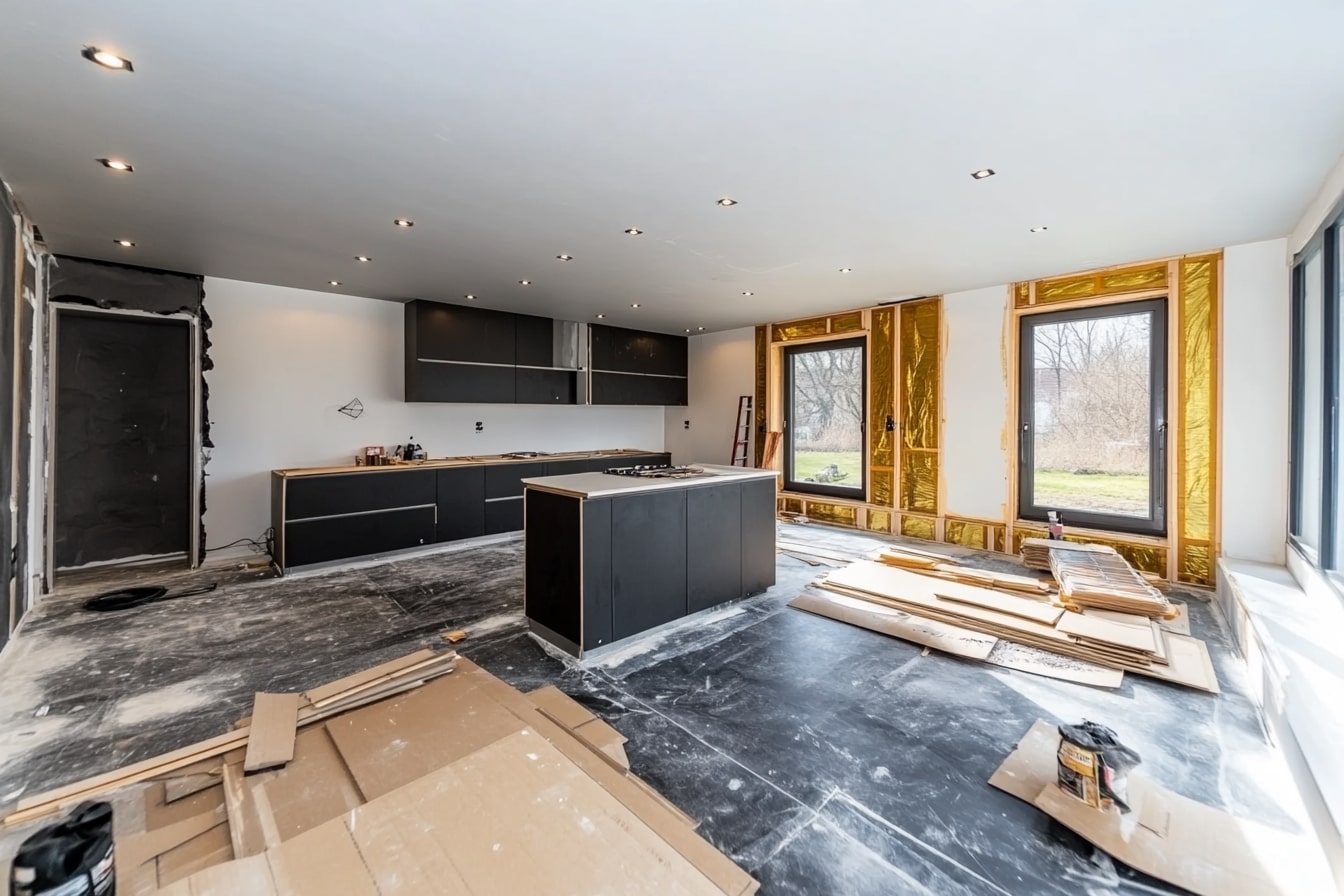

Modern trends in prefabricated home design
Contemporary prefab homes embrace minimalist aesthetics, open floor plans, and seamless indoor-outdoor living spaces. Popular design elements include floor-to-ceiling windows, clean geometric lines, and flexible room configurations that adapt to changing lifestyle needs. Many manufacturers now offer extensive customization options, allowing homeowners to select everything from exterior cladding materials to interior finishes. Smart home technology integration has become standard, with pre-wired systems for automated lighting, climate control, and security features.
How prefab construction methods differ from traditional building
Prefabricated construction occurs in climate-controlled factory environments where components are manufactured simultaneously rather than sequentially. This parallel production process significantly reduces construction timelines from months to weeks. Quality control measures in factory settings often exceed those possible at traditional job sites, with precise measurements and standardized assembly procedures. Weather delays become virtually eliminated since most construction happens indoors, and material waste decreases substantially through optimized manufacturing processes.
Sustainable materials commonly used in modular housing
Modern prefab homes frequently incorporate recycled steel framing, sustainably harvested lumber, and low-VOC insulation materials. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) has gained popularity for its strength, carbon sequestration properties, and renewable nature. Energy-efficient windows with triple glazing and advanced thermal breaks help achieve superior insulation performance. Many manufacturers utilize recycled content in composite materials and prioritize locally sourced components to reduce transportation environmental impact.
Factors that influence the total cost of prefab homes
Several variables affect prefab home pricing, including size, customization level, site preparation requirements, and regional delivery costs. Foundation work, utility connections, and local permitting fees add to the base home price. Transportation distances from manufacturing facilities significantly impact final costs, particularly for larger modules. Site accessibility, soil conditions, and local building code requirements can create additional expenses during installation.
| Provider | Base Price Range | Key Features | Delivery Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clayton Homes | $80,000 - $200,000 | Energy Star certified, customizable layouts | Nationwide |
| Blu Homes | $250,000 - $600,000 | Steel frame construction, modern design | West Coast |
| Method Homes | $200,000 - $500,000 | Sustainable materials, architectural designs | Regional |
| Champion Home Builders | $70,000 - $180,000 | Traditional and modern styles | Multi-state |
| LivingHomes | $300,000 - $700,000 | LEED certified, contemporary aesthetics | California, Northeast |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The prefab housing industry continues expanding as technology advances and consumer preferences shift toward efficient, sustainable living solutions. Manufacturing innovations enable increasingly complex architectural designs while maintaining cost advantages over traditional construction. Quality improvements and design sophistication have helped prefab homes shed previous stigmas, attracting environmentally conscious buyers and design enthusiasts alike. As urbanization increases and housing costs rise, prefabricated construction offers a viable path toward accessible homeownership without compromising on style or sustainability.